Tracer material was placed in "feeder" piles on the bottom of the model and
allowed to move according to prevalent flow patterns. Deposition patterns that
formed in the model at the Port of Anchorage and on the Woronzof Shoal were
noted by the Alaksa District engineers to be similar to those deposition patterns
historically seen at those locations. Deposition of tracer at the Port of Anchorage
during flood flow occurred as a crescent-shaped berm starting on one end and
extending to the other end. Monthly condition surveys indicated that shoaling at
the port occurred in much the same way.
Ebb-tidal simulations with the large-area model reversed on the flow table
indicated that Cairn Point plays an important role in sedimentation of the Port of
Anchorage. A stationary eddy was formed in the lee of Cairn Point as flow
separation occurred at the point. According to the Alaska District engineers,
"The outer edge of the eddy appeared to coincide with the
historical development of sediment accumlation in the vicinity of the
dock face."
Injected dye captured by the eddy exhibited long residence time in the immediate
vicinity of the port. This would gave fine silts in the water column time to settle,
thus contributing to sedimentation of the Port of Anchorage.
Testing of the large-area model evolved according to the insights provided by
the model with different tide levels being the primary variable. During ebb flow
it was shown that modifying the upstream channel configuration could change
the geometry of the eddy affecting the Port of Anchorage, but most of the eddy
persisted at nearly the same location.
Small-Area Model Description
The seaward flow boundary of the small-area idealized model was situated
just to the west of Point Woronzof with a lateral extent of approximately 3.6 n.m.
(Figure 6). The upstream boundary was located about 2.6 n.m. upstream of the
Port of Anchorage. This area was scaled to fit roughly into an area with overall
dimensions of 0.91 x 0.91 m (3 ft by 3 ft). Relevant scale ratios for the small-
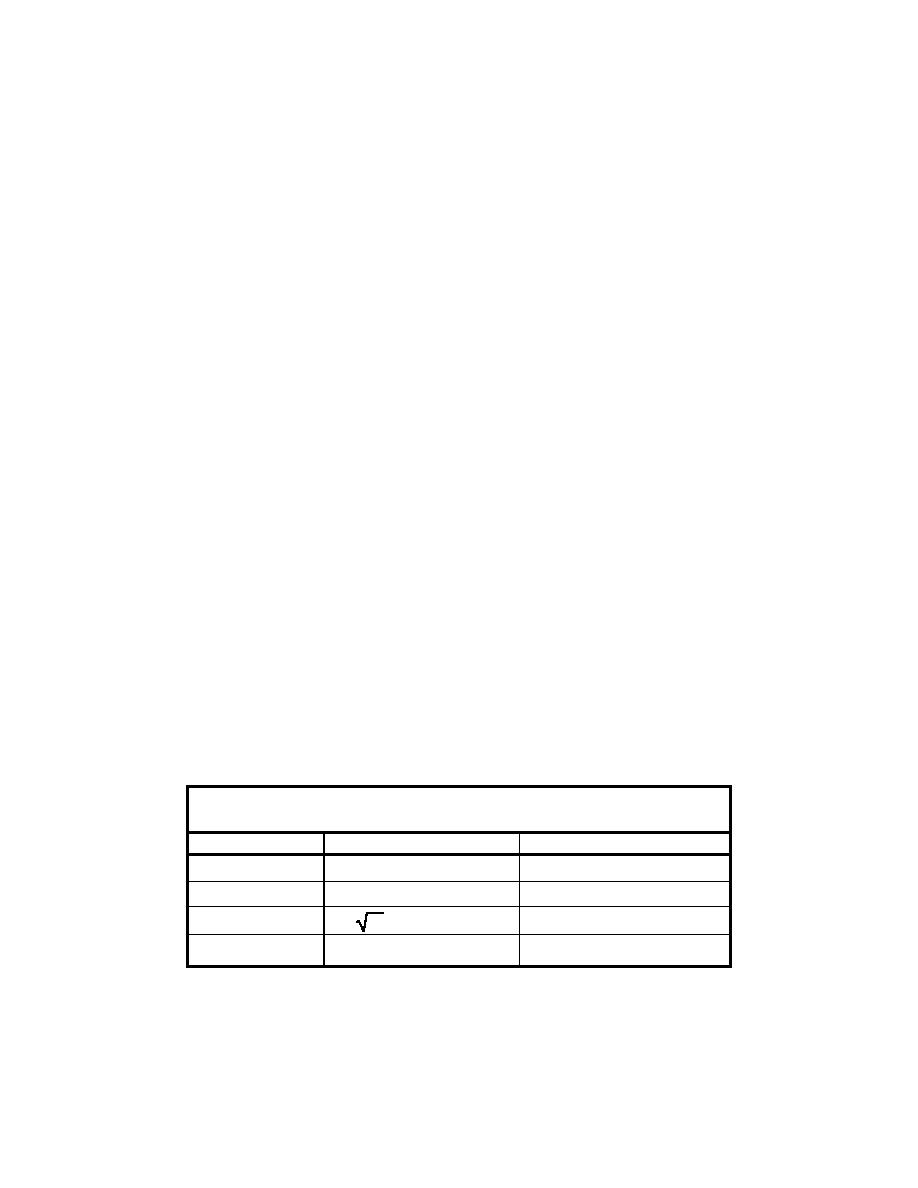
area model are listed in Table 3 along with approximate model equivalences.
Table 3
Scale Ratios for Small-Area Model
Scale
Scale Value
Model Equivalence
NX = 11,307
940 ft ≈ 1 in.
Horizontal Scale
NZ = 480
Vertical Scale
40 ft = 1 in.
NV =
NZ = 21.9
Velocity Scale
2.2 m/sec = 10 cm/sec
NQ = NXNZ3/2 = 118,907,500
Discharge Scale
203,000 cu m/sec = 1.71 liters/sec
17
Chapter 3 Idealized Cook Inlet Models




 Previous Page
Previous Page
