920
JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY
VOLUME 33
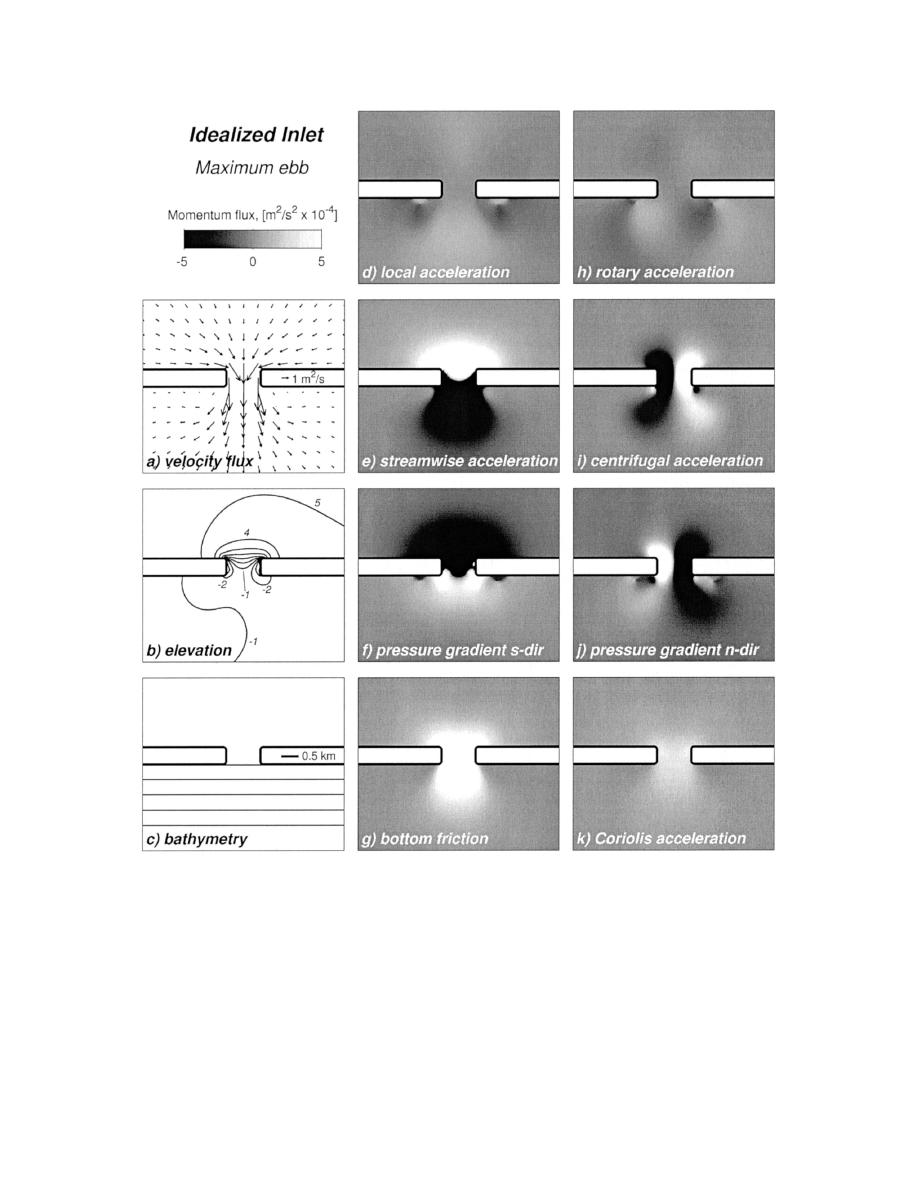
FIG. 5. Circulation and momentum balances for idealized inlet at maximum ebb: (a) velocity flux (depth-averaged velocity
multiplied by total water column) vectors interpolated onto uniform 425-m grid for clarity, (b) free-surface elevation with 1-
cm contour intervals, (c) bathymetry with 1-m contour intervals, and (d)(k) shaded contours of individual momentum flux
terms (see text for description).
dient at maximum ebb, but is largest in the navigation
inlet the elevation difference between sound and ocean
channel where flow speeds are greatest.
is about 2 cm (Fig. 7b). The streamwise balance is be-
tween the pressure gradient, advective acceleration, and
bottom friction, as during maximum ebb, but local ac-
b. Midebb
celeration in now significant. Flow in the inlet throat
decelerates, while flow along the shoreline outside the
As ebb advances toward slack, the pressure gradient
between the sound and ocean weakens. For the idealized
inlet is beginning to accelerate (Fig. 7d). Streamwise




 Previous Page
Previous Page
