921
APRIL 2003
HENCH AND LUETTICH
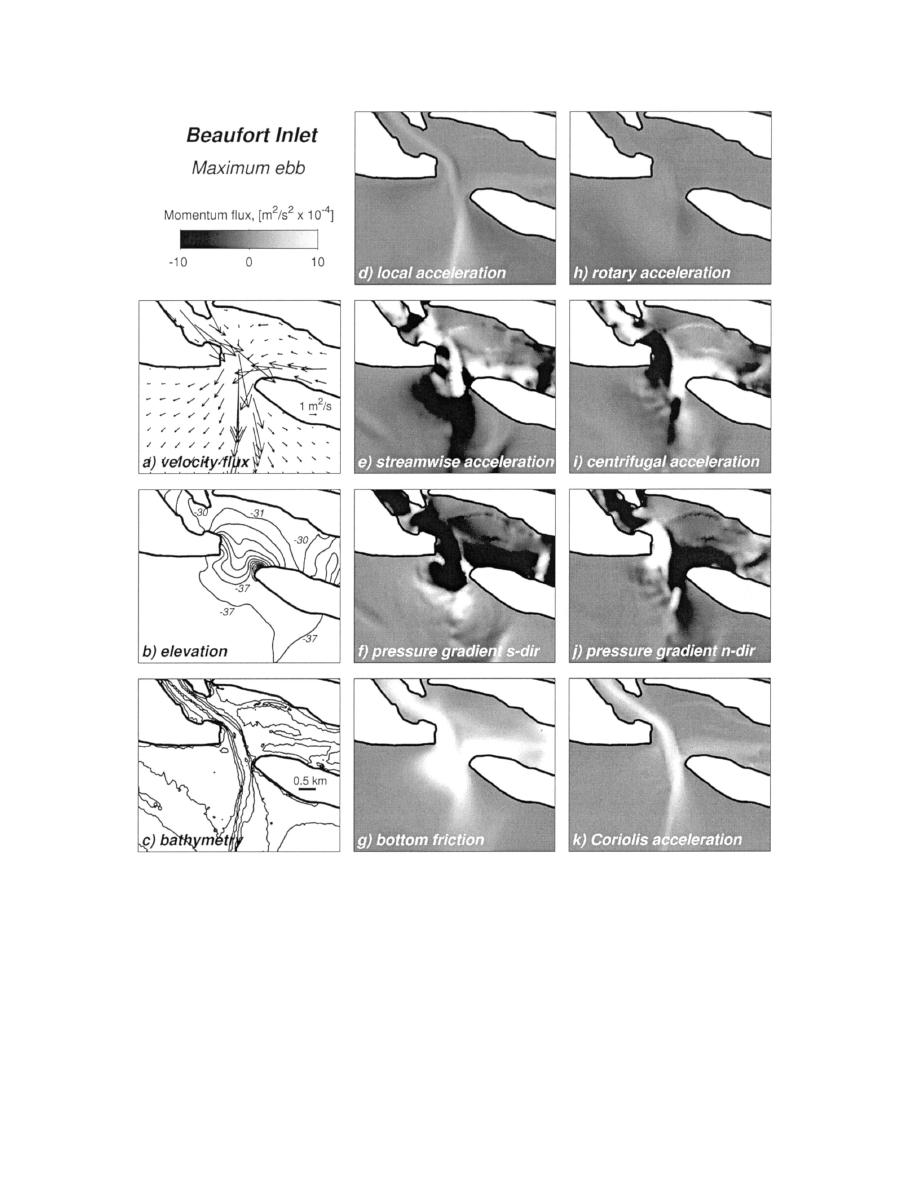
FIG. 6. Circulation and momentum balances for Beaufort Inlet at maximum ebb: (a) velocity flux (depth-averaged velocity
multiplied by total water column) vectors interpolated onto uniform 425-m grid for clarity, (b) free-surface elevation with 1-
cm contour intervals, (c) bathymetry with 4-m contour intervals, and (d)(k) shaded contours of individual momentum flux
terms (see text for description).
positive advective acceleration along the sides of the
main fairly constant in time. The cross-inlet pressure
ebb jet (light areas along the sides of the dark ebb jet
gradient and centrifugal acceleration have weakened,
in Fig. 7e) shows the transfer of momentum from the
but they remain the primary lateral balance (Figs. 7i,j)
jet to the slower moving fluid in the lee of the headlands.
and are modified slightly by Coriolis (Fig. 7k).
The cross-stream balance shows little contribution from
At Beaufort Inlet, the midebb elevation difference
the rotary acceleration term (Fig. 7h), indicating that
between the sound and ocean is also about 2 cm (Fig.
although flow speeds are decreasing, flow directions re-
8b), and flow in the main channel is strongly deceler-




 Previous Page
Previous Page
