Inlet Stability
Quantitative empirical relations between the equilibrium, or minimal stable
cross-sectional channel area of an inlet and its tidal prism have been established
for almost a century (e.g., LeConte 1905; O'Brien 1931, 1969; Jarrett 1976).
This relation is expressed as:
AC = CPn
(6-2)
where AC = minimum inlet cross-sectional channel area below msl, and C and
n = empirical coefficients determined from field measurements.
The original expression has undergone refinement as measurements have
become available. Research has been performed to better estimate the empirical
coefficients, taking into account processes such as wave activity, degree of
sheltering of the inlet from waves, presence or absence of jetties, inlet channel
cross-section size, and sediment size. Jarrett (1976) analyzed 108 tidal inlets
along the three oceanic coasts of the United States and quantified variations in
this relation based on location and the number of jetties as none, one, or two.
Table 6-2 lists the empirical coefficient values derived by Jarrett (1976). The
108 inlets examined were located on sandy (fine to medium sand) coasts.
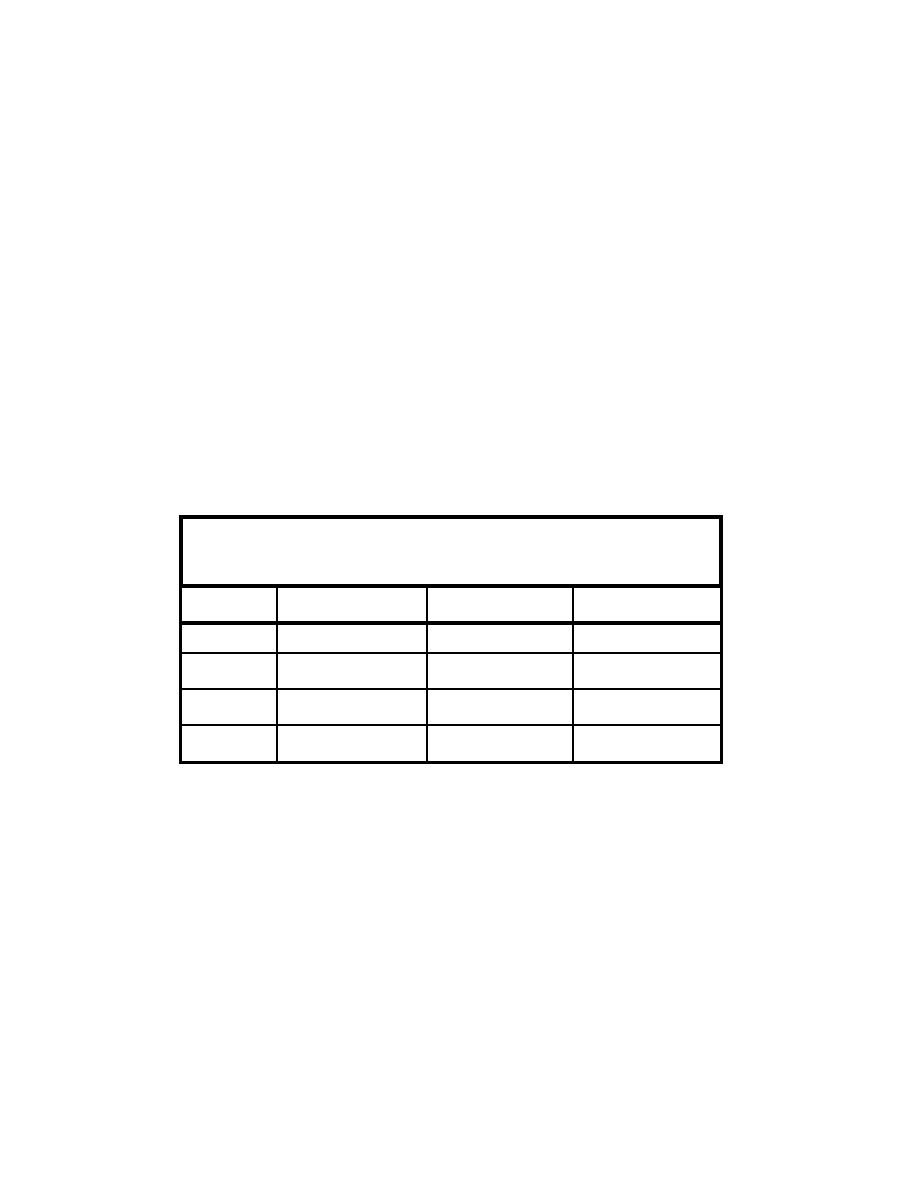
Table 6-2
Tidal Prism (cu ft) and Minimum Channel Cross-Sectional Area
(sq ft) Relationships (Jarrett 1976)
Unjettied,
Location
All Inlets
Single jettied
Dual Jettied
5
0.95
5
1.03
4
0.86
All Inlets
Ac = 5.74 x 10
P
Ac = 1.04 x 10
P
Ac = 3.76 x 10
P
6
1.05
6
1.07
5
0.95
Atlantic Coast
Ac = 7.75 x 10
P
Ac = 5.37 x 10
P
Ac = 5.77 x 10
P
4
0.85
4
0.86
Gulf Coast
Ac = 5.02 x 10
P
Ac = 3.51 x 10
P
Insufficient data
4
0.91
6
1.10
4
0.85
Pacific Coast
Ac = 1.19 x 10
P
Ac = 1.91 x 10
P
Ac = 5.28 x 10
P
Simpson (1976) investigated the hydraulics of two small gravelly inlets
located within Puget Sound, WA, and found that the cross-sectional area of both
inlets was smaller than the equilibrium area predicted by previously derived
expressions. Byrne et al. (1980) investigated 14 small inlets they defined by the
criterion Ac < 100 sq m (1,076 sq ft). These inlets were located within lower
Chesapeake Bay, VA, on sandy shores and were not stabilized by structures.
They quantified a departure from previously derived coefficients based on inlet
size. This relation, expressed in American Customary Units, was found to be:
AC = 1.212 10-2 P0.61
(6-3)
Byrne et al. (1980) compared their data set to that compiled by Jarrett (1976) and
concluded that for small inlets, the departure from the tidal prism minimum
channel cross-sectional area relation derived for larger oceanic inlets occurs
between Ac = 100 and 500 sq m (1,076 and 5,082 sq ft).
268
Chapter 6 Inlet Morphology and Stability




 Previous Page
Previous Page
