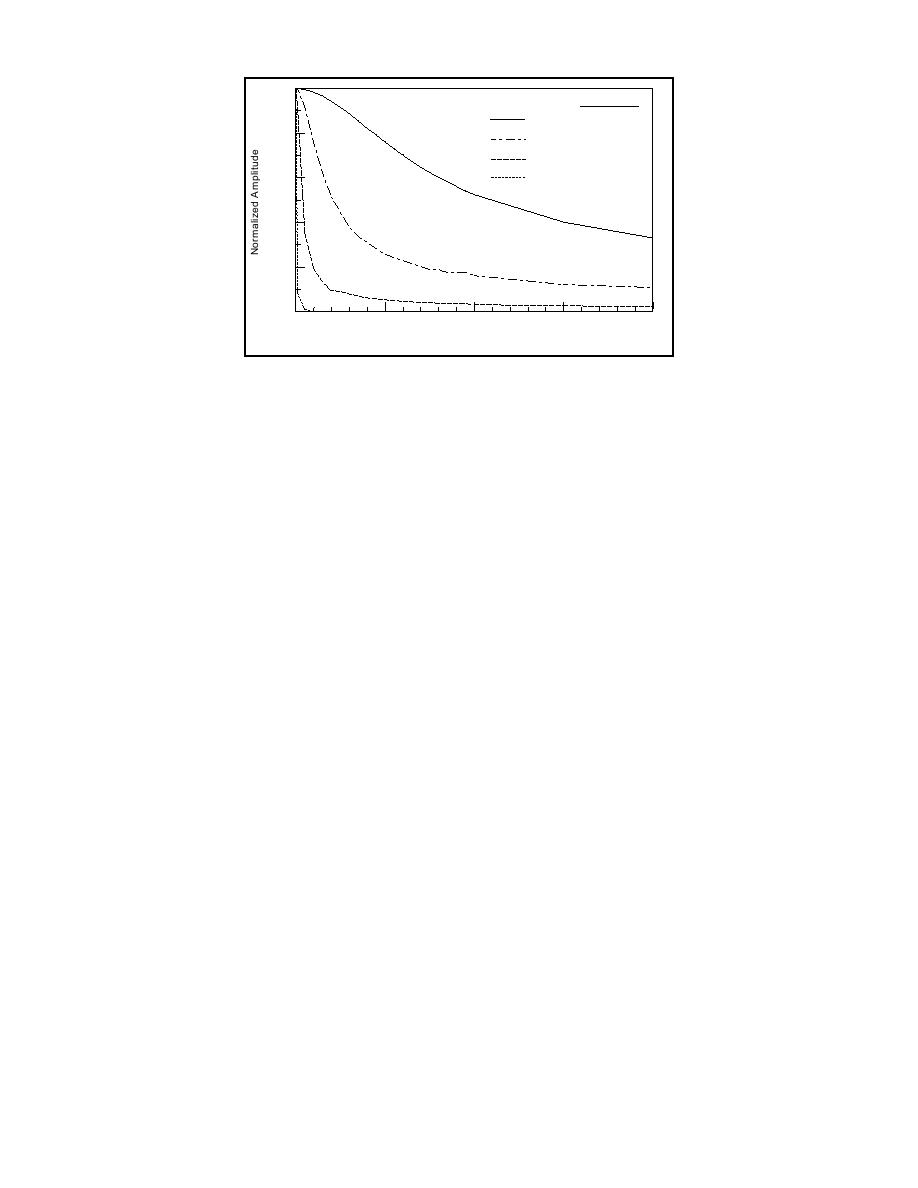
1.0
Amp (C fL= 0)
1 cpd
0.242
0.8
3 cpd
0.074
5 cpd
0.034
4.7 cpd
0.036
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.000
0.005
0.010
0.015
0.020
CfL
Fig. 8. Normalized amplitudes for oscillatory wind-forced water level for friction coefficient
ranging from 0 to 0.020.
CONCLUSION
An analytical solution for an idealized 1D basin was developed to study the response of
initially quiescent water to oscillatory wind as governed by the linearized equations of
motion with quadratic wind stress. The solution displays in compact form general behavior
and dependencies of the physical processes, including generation of harmonics of the
motion, damping, and resonance. The solution can serve as a benchmark test for numerical
models of the shallow-water equations to examine properties such as numerical damping,
generation of spurious motions, symmetry, and accuracy. It also provides a convenient
procedure for making first-order estimates of wind-induced motion in enclosed water
bodies such as bays, estuaries, lakes, and reservoirs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was conducted as part of activities of the Inlet Geomorphology and Channels
Work Unit of the Coastal Inlets Research Program, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
(USACE). Permission was granted by Headquarters, USACE, to publish this information.
REFERENCES
Collier, A., and Hedgpeth, J.W. 1950. An Introduction to the Hydrography of Tidal Waters of Texas.
Pubs. Inst. Mar. Sci., 1(2), 125-194.
Ippen, A.T., and Harleman, D.R.F., 1966. Tidal Dynamics in Estuaries. Estuary and Coastline
Hydrodynamics, Ippen, A.T. (Ed), McGraw-Hill, New York, 493-545. .
Kraus, N.C., and Militello, A., 1999: Hydraulic Study of Multiple Inlet System: East Matagorda Bay,
Texas. J. Hydraulic Eng. 25(3), 224-232.
Lamb, H. 1945. Hydrodynamics. 6th edition. Dover Publications, New York, 738 pp.
Militello, A. 2000: Hydrodynamic Modeling of a Sea-Breeze Dominated Embayment, Baffin Bay,
Texas. Proc. Sixth International Conf. on Estuarine and Coastal Modeling, ASCE, 795-810
Militello, A., and Kraus, N.C. 2001. Generation of Harmonics by Sea Breeze in Nontidal Water
Bodies. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 31(6): 1,639-1,647.
Parker, B.B., 1991. The Relative Importance of the Various Nonlinear Mechanisms in a Wide
Range of Tidal Interactions (Review). Tidal Hydrodynamics, Parker, B. B., Ed., John Wiley &
Sons, New York, 237-268.
Zetler, B.D., and Hansen, D.V. 1970. Tides in the Gulf of Mexico A Review and Proposed
Program. Bull. Mar. Sci., 20(1), 57-69.
10
Kraus & Militello




 Previous Page
Previous Page
