and model simulations conducted to examine surface wave propagation through the inlet,
including the modification of the waves by the tidal current and water level.
FIELD DATA COLLECTION
The data-collection program consisted of bathymetry surveys in the offshore and along
maintained and natural channels; a LIDAR survey and controlled aerial photography of
land and tidal flats during lower tide in the bay; measurement of water level at five
locations around the bay periphery, wind and barometric pressureat a nearshore tower; and
waves, water level, tidal current through the water column, and suspended sediment
concentration at seven bottom-residing tripods. The tripod deployment interval of mid-
September to mid-November 1999 spanned two lunar months (Hericks and Simpson 2000).
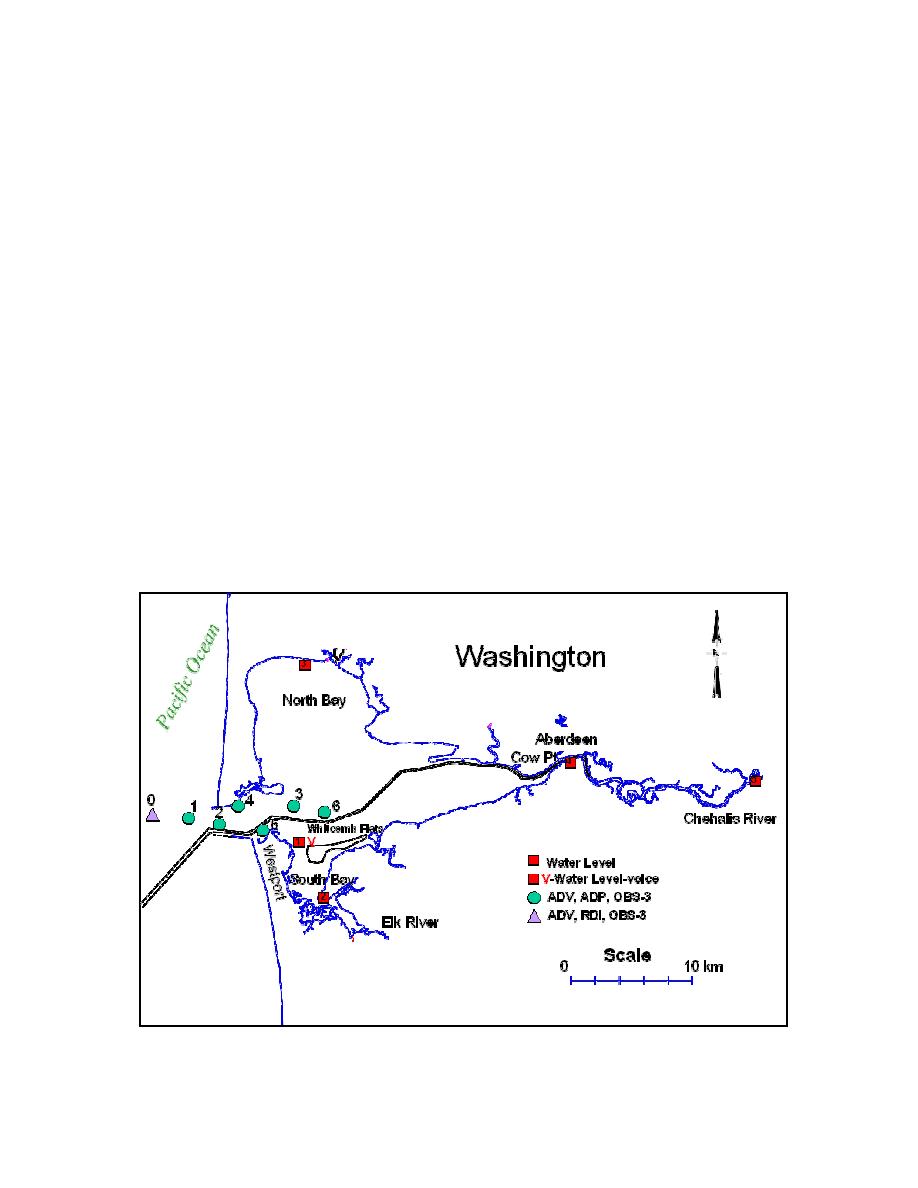
The tripods were deployed along or near the navigation channel (Fig. 1). Stations 1
through 6 extend from the entrance, through the inlet, and into the bay. Each tripod was
configured with a SonTek Hydra, functioning as a directional wave gauge and an up-
looking 1,500-kHz Acoustic-Doppler Profiler (Fig. 2). The Hydras contained a down-
looking Acoustic-Doppler Velocimeter Ocean Probe, a high-resolution Resonant Pressure
Transducer, and two optical backscatterence sensors. This instrument suite documented the
waves, current near the bottom, and water level; the current through the water column in
0.5-m bins; and the suspended-sediment concentration through the inlet entrance. Station 0
(the seaward-most location) was configured with an Ocean Probe and an RDI Sentinel
ADCP with directional wave-spectra firmware to determine if comparable data are derived
from the two different measurement methods.
Fig. 1. Grays Harbor, Washington location map and field-data collection schematic
Cialone & Kraus
2




 Previous Page
Previous Page
