W. Huang et al. / Ocean Engineering 30 (2003) 22752295
2293
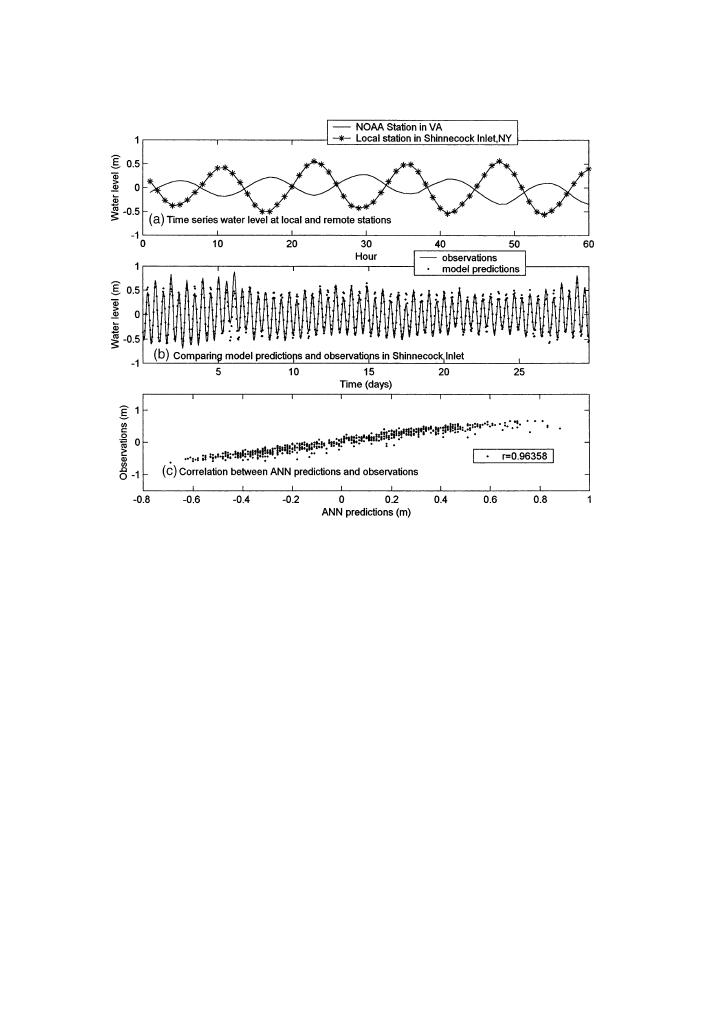
Fig. 14. Model test using water level inputs from a remote NOAA station located 466 km away in the
coast of Lewisetta, Virginia.
of time series water levels in a NOAA station in the region, the RNN--WL model
is capable of predicting water levels in a local station at coastal inlets. The RNN--
WL neural network model employs three-layer feed-forward, backpropagation struc-
ture with optimized training method using conjugated training algorithm. The model
requires the input of the last 4-h values of the hourly water levels from a permanent
NOAA station to predict the hourly water levels in an inlet station. The model was
successfully tested in a case study in the Long Island south shore using input data
from NOAA water level station ranging from 60 to 591 km away. Field data indicate
that water levels change substantially in both amplitude and phase over the coastal
region due to the complex coastal and estuarine topography and shallow water
effects. In addition, low-frequency non-tidal water levels also vary due to wind
effects. Using short-term data sets (two months), the model was trained using a
month-long data set, and verified using another independent data set for another
month-long period. The model was then successfully tested using yearlong data sets.
The predicted tidal signals matched well with observations. The model was also
successfully validated in predicting non-periodic subtidal sea levels. Because there
are several decades of hourly water level data available since the 1940s in NOAA
permanent stations located at the Montauk and Battery stations in the region, the
successful development of the RNN--WL model in this study will supplement cost-




 Previous Page
Previous Page
