W. Huang et al. / Ocean Engineering 30 (2003) 22752295
2292
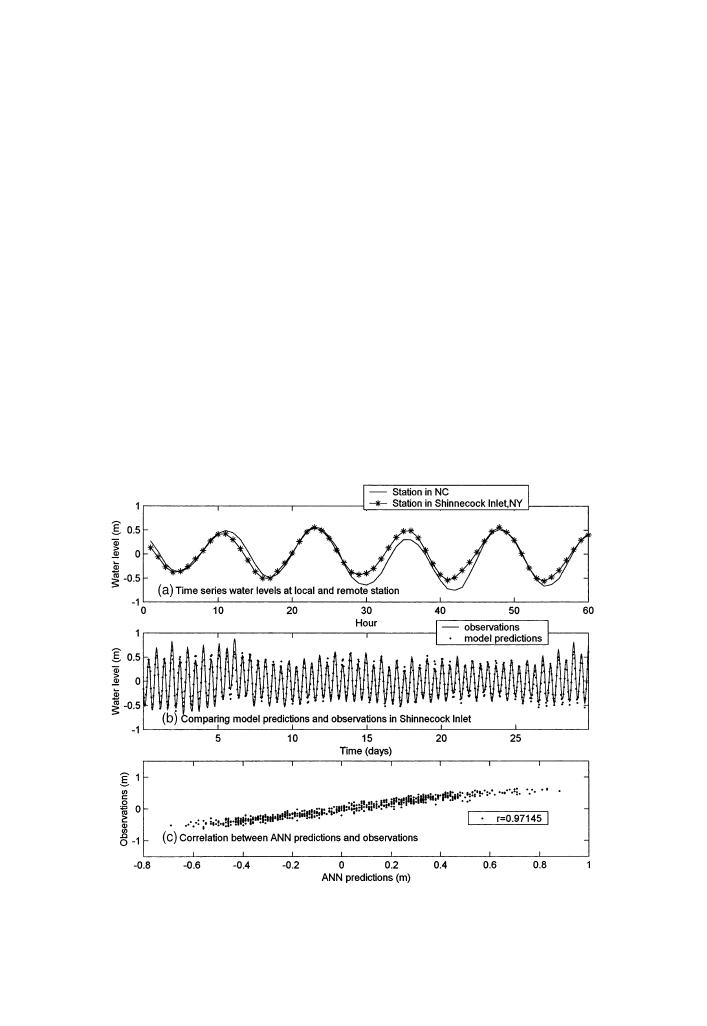
root-mean-square error (Fig. 13). Model predictions using inputs from the Lewisetta
station are not so accurate as those using input from Duck and Atlanta City stations.
As given in Fig. 14, there is about a 180 degree phase difference between water
levels at local coastal station at Shinnecock Inlet and NOAA station at Lewisetta in
Chesapeake Bay, which may be caused by the reflection of tidal waves in the estuary
of Chesapeake Bay. Despite the significant difference of amplitude and phase
between the input and output stations, model predictions using inputs from the Lew-
isetta Station match well with observations, resulting in a correlation value of 0.96
and a root-mean square error of 0.09 m. Based on the information given in NOAA
Water Level Network Web site, NOAA water level stations are distributed along the
coastline of USA. The distance between most of NOAA stations range from 50 km
to 200 km. Therefore, the validation of RNN--WL model in this study for the dis-
tance up to 591 km provides good confidence that the RNN--WL model can be
used in regional coastal studies at other sites.
8. Conclusion
A Regional Neural Network for Water Level (RNN--WL) has been successfully
developed in this study for water level predictions at coastal inlets. Using the inputs
Fig. 13. Model test using water level inputs from a remote NOAA station located 591 km away in
coastal of Duck, North Carolina.




 Previous Page
Previous Page
